Managing Internal Access to Your Tenant
Sharing Access to Audit Trails within your Tenant
Caution: You will only have access to theAccess Policiesscreen if you are an Administrator in your organization.
Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC) policies can be used to control access Audit Trails and Events within a single organization.
Specifically, ABAC policies are created by Administrators to share information with Non-Administrators in the same Tenancy.
ABAC policies can be granular, with users only allowed to see single attributes at a time.
It is possible to control read and write access to Trails based on a combination of properties of the Trail as specified in the Asset attributes, such as type and location (eg: “all models trained in Gondwalaland”)
By default, new users will not see any existing Trails or Events until an Administrator explicitly creates an ABAC policy to allow them.
Note: To create an ABAC policy, first add users to your tenancy.
Creating an ABAC Policy
Consider the Shipping Container Asset we created. There may be many people within an organization who need access to specific attributes of the container.Note: Access policies are applied to the Trail and are themselves transparent. When a policy is created or updated, an Event will be recorded in the audit trail of matching Assets from the ActorArchivist Internalto let people know if their access has changed. This prevents ’log black-out’ attacks.
We shall create a policy for someone who needs to share some standard dimensions of the Shipping Container, inspect the cargo, and create Inspect Events.
You may wish to view your existing policies before creating a new one.
Navigate to the
Access Policiessection on the sidebar of the DataTrails dashboard. Here you will see any existing policies and can selectCreate Policy.Creating a Policy You may view your existing policies before creating your new policy by executing the following curl command. See instructions for creating your
BEARER_TOKEN_FILEhere.curl -v -X GET \ -H "@$HOME/.datatrails/bearer-token.txt" \ https://app.datatrails.ai/archivist/iam/v1/access_policiesCreate your Access Policy.
Select
Create Policy.Managing Policies Create an empty file, in later steps we will add the correct JSON.
{ }Set the asset filters for your policy
When adding a policy, you will see this form:
Policy Web Form Here you can apply policy filters to apply to specific Trails or groups of Trails. In this case, we shall apply the policy to any Asset with the type
Shipping Container.Filtering for specific Assets and Locations Filters can use
andororto define scope. You may also use filters on attribute values, such as=and!=for equal and not equal, respectively. These can be used for specific attribute values, or to check if the value exists at all. For example, to filter for Assets not associated with a location, you could use:"attributes.arc_home_location_identity!=*"The
*is a wildcard that could represent any value. This will match not only on string values, but list and map values as well.Following our Shipping Container example, this is how we would set our Asset filters:
{ "display_name": "Mandy Inspect Policy", "filters": [ { "or": [ "attributes.your_custom_attribute=Your Value>" ]}, { "or": [ "attributes.arc_home_location_identity=locations/<location-id>" ]}, { "or": [ "attributes.arc_display_type=Shipping Container" ]} ] }See here for instructions on finding your location ID.
Note We will not use the custom attribute any further as we build the example.Enter the desired
Permissionsto set user’s accessWe select the
PermissionsTab to set Users’ access policy.Default view of Policy Permissions In this example, the
Useractor is identified by email. Type the relevant email address and hit enter; you may also see a dropdown list of users within your tenancy.Adding a specific User to a Policy There are a few ways you may add a
Userto your Access Policy using JSON. One way is to use the email address associated with their DataTrails account. To do so, add the desireduser_attributesto theaccess_permissionssection.Note You may grant access to specific attachments by specifying the corresponding key in theaccess_permissions."access_permissions": [ { "asset_attributes_read": ["arc_display_name", "arc_display_type", "arc_primary_image", "length", "weight"], "user_attributes": [ {"or": ["email=user@email.com"]} ] } ]You may also grant permissions to an App Registration within your tenancy. App Registrations are non-root by default; best practice is to use ABAC policies to preserve Principle of Least Privilege.
"access_permissions": [ { "asset_attributes_read": ["arc_display_name", "arc_display_type", "arc_primary_image", "length", "weight"], "user_attributes": [ {"or": ["subject=<client-id>"]} ] } ]Note: This is different from addingsubjectsas a key in youraccess_permissions, for example, when adding an external Subject ID to an OBAC policy. The user attributesubjectrefers to the Client ID associated with an App Registration.Additionally, you may set permissions based on the Custom Claims of an App Registration using JSON Web Tokens (JWTs). To do so, you must include the prefix
jwt_followed by the desired claim as one of theuser_attributesin the policy. For example, the keyjwt_app_reg_roleto match on claimapp_reg_role."access_permissions": [ { "asset_attributes_read": ["arc_display_name", "arc_display_type", "arc_primary_image",, "length", "weight"], "user_attributes": [ {"or": ["jwt_app_reg_role=tracker"]} ] } ]Once all relevant details are complete, add the permission group to the policy. You may add multiple permission groups per policy if you wish.
Here we are restricting Mandy to viewing theName,Type,Image,lengthandweightof Shipping Containers currently located at the UK Factory. She cannot modify the container record and she cannot see the full Audit Trail of Events because she only needs to know that the container does not exceed the maximum length and weight.Enter desired permissions and select
Add Permission GroupPermitted Attributes on an Asset Add the desired permissions and the desired
user_attributes{ "display_name": "Mandy Inspect Policy", "filters": [ { "or": [ "attributes.arc_display_type=Shipping Container" ]} ], "access_permissions": [ { "asset_attributes_read": ["arc_display_name", "arc_display_type", "arc_primary_image", "length", "weight"], "user_attributes": [ {"or": ["email=mandy@datatrails.ai"]} ] } ] }Note: We have included DataTrails-significant attributes:arc_display_name,arc_display_typeandarc_primary_imagearc_*attributes have special significance in DataTrails.
In this case, respectively, allowing visibility to theName,Type, andImageof the Asset. Otherarc_*attributes are also available.Once complete, finish creating the Access Policy.
Select
Create Policy.Submitting a Policy fo Use the curl command to run your JSON file! See instructions for creating your
BEARER_TOKEN_FILEhere.curl -v -X POST \ -H "@$HOME/.datatrails/bearer-token.txt" \ -H "Content-type: application/json" \ -d "@/path/to/jsonfile" \ https://app.datatrails.ai/archivist/iam/v1/access_policiesCheck the Asset is appropriately shared
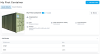
Mandy should only be allowed to see the Asset’s name, type, image, length, and weight attributes.
Mandy's view as a Non-Administrator For comparison with our Administrator, Jill who can see everything:
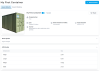
Jill's view as a Administrator
We can see that Mandy can only view the Attributes specified in the policy.
Our Administrator, Jill, can see every detail associated with the Asset.